What Is Data Deduplication Explained Simply

Data deduplication is a clever storage technique that gets rid of redundant copies of your data. Think of it like this: a library keeps just one copy of a super popular book, and everyone who wants to read it gets a small note pointing to that single copy. That’s essentially how deduplication works with your digital files, and it saves a massive amount of storage space.
Understanding Data Deduplication
Think of data deduplication as a highly efficient digital librarian for your entire storage system. In any given organization, people create and save countless identical files and data blocks every single day. It just happens.
For instance, an email attachment sent to 50 people creates 50 identical copies on the server. A standard virtual machine template might be cloned hundreds of times. Data deduplication is the process that systematically finds these exact duplicates.
Instead of storing all 50 copies of that attachment, the system keeps only one unique version. For the other 49 instances, it swaps out the full file for a tiny pointer that simply references the single, stored copy. This process usually happens automatically at a granular level—the "block" level—meaning it can find identical chunks of data even if they're buried inside different files. While it sounds simple on the surface, this specialized form of data compression is a game-changer for storage efficiency.

The Growing Importance of Smart Storage
The demand for this technology is skyrocketing. The global data deduplication market is on track to grow from around $4.2 billion in 2023 to an incredible $28.5 billion by 2033. That explosive growth is a direct result of the relentless creation of digital information and the very real, rising costs of storing it all.
By intelligently weeding out all that redundant data, businesses can hit several key objectives at once:
- Reduced Storage Costs: Less data means you need less expensive physical hardware or cloud storage capacity. It's a direct impact on the bottom line.
- Faster Backup and Recovery: Backing up a much smaller, unique dataset takes significantly less time and chews up far less network bandwidth. When you need to recover, it's faster too.
- Improved Network Efficiency: Replicating data to a disaster recovery site is much quicker when you're only sending the unique changes, not the same data over and over.
The table below breaks down the core problems that deduplication directly solves.
Core Problems Solved by Data Deduplication
| Business Challenge | How Deduplication Provides a Solution |
|---|---|
| Spiraling Storage Costs | Reduces the physical or cloud storage footprint by storing only one instance of unique data, directly lowering hardware and subscription expenses. |
| Slow Backup Windows | Speeds up backup processes by shrinking the total volume of data that needs to be transferred and stored, allowing backups to complete faster. |
| Network Congestion | Frees up network bandwidth, especially for replication and backups, by transmitting only unique data blocks instead of entire redundant files. |
| Inefficient Disaster Recovery | Enables quicker data replication to off-site locations and faster system recovery times because there is less data to restore. |
As you can see, deduplication isn't just a "nice-to-have"—it's a practical solution to some of the most pressing data management challenges today.
For anyone who manages large datasets, from complex enterprise systems down to individual spreadsheets, knowing how to handle duplicates is crucial. While this guide is focused on large-scale systems, the core principles of data cleanliness and efficiency are just as important in tools like Excel. Proper data management in Excel can prevent major errors and save a surprising amount of time.
Why Deduplication Is No Longer Optional
Not too long ago, data deduplication felt like a luxury feature—something you'd find in the high-end storage systems of massive corporations. Today, that's completely changed. It’s now a fundamental, must-have tool for just about any business, all thanks to one unstoppable force: the explosive growth of data.
To put it simply, we are creating digital information at a pace that makes older storage methods obsolete. The numbers are staggering. Between 2020 and 2025 alone, the amount of data created worldwide is expected to jump from 64.2 zettabytes to a mind-boggling 181 zettabytes. Think about that—we’re on track to nearly triple the world's data in just five years. As you can imagine, this puts an incredible strain on IT infrastructure. You can find a deeper analysis of this data explosion on ve3.global.
This relentless growth isn't just an abstract problem; it creates very real, tangible challenges that businesses can't afford to ignore.

The Pressures of Modern Data Demands
When data growth goes unchecked, the consequences ripple through every part of the organization. Without an efficient way to weed out redundant information, companies face a cascade of operational headaches and financial drains. The primary pain points usually boil down to three things:
- Skyrocketing Storage Costs: More data means more hardware. Or more cloud capacity. Either way, the budget for storage just keeps climbing.
- Painfully Slow Backups: As datasets swell, backup windows stretch from a few hours into days. This not only puts recovery goals at risk but also increases the potential for data loss in a disaster.
- Network Bottlenecks: Pushing huge volumes of redundant data across the network—especially when replicating to a disaster recovery site—can clog your bandwidth and slow down critical business operations to a crawl.
These aren't just minor technical annoyances. They're a significant drag on productivity and the bottom line. The time and energy IT teams spend managing bloated, inefficient datasets are resources that could be invested in projects that actually move the business forward.
"Deduplication is no longer just about saving space. It's about restoring agility to IT operations. When backups are faster and networks are clearer, the entire business runs more smoothly."
Cloud and Compliance Raise the Stakes
Two other major shifts have cemented deduplication's role as an essential technology: the massive move to the cloud and the ever-tightening grip of data regulations.
Cloud providers typically charge based on how much data you store and transfer. Sending redundant data to the cloud is literally like paying to ship the exact same package over and over again. Deduplication stops that, ensuring you only pay to store and move unique data. This makes any cloud strategy far more cost-effective.
At the same time, regulations like GDPR and CCPA demand that organizations manage their data responsibly, with clear rules for retention and protection. A smaller, deduplicated dataset is just flat-out easier to secure, audit, and manage for compliance. It shrinks your digital footprint, giving you less to worry about. In this environment, understanding what is data deduplication becomes the first critical step toward building a data strategy that's both resilient and compliant.
How Different Deduplication Methods Work
To really get a handle on data deduplication, you have to look past the definition and see how it works in the real world. It’s not a one-size-fits-all technology. Different methods offer their own mix of performance, efficiency, and resource demands, and they're usually defined by where, when, and how they inspect your data.
Think of it like getting a huge shipment of packages ready. Do you sort them at the factory before they even go on the truck (source-side)? Or do you wait until they all land at the distribution center (target-side)? You could also sort them as they come off the assembly line (inline) or pile them up and deal with them at the end of the day (post-process). Each choice impacts your workflow and speed.
It’s the same with data deduplication. The method you choose depends on what you're trying to achieve, whether it's for high-speed primary storage or massive backup archives. Let's break down the main approaches.
Source-Side vs. Target-Side Deduplication
The first big question is: where does the magic happen? The answer directly affects your network traffic and how much work your storage systems have to do.
-
Source-Side Deduplication: This approach gets to work on the client or server, sniffing out and removing redundant data before it ever gets sent over the network. It’s like proofreading an email to remove a giant, unnecessary attachment before you hit send. The huge plus here is a major cut in network bandwidth, making it perfect for backing up remote offices or moving data to the cloud.
-
Target-Side Deduplication: Here, all the data is sent across the network first and lands on the storage device. The storage system itself then does the heavy lifting, analyzing the incoming data to find and get rid of duplicates. While it doesn't do anything to reduce the initial network traffic, it takes the processing load off your servers, freeing them up to focus on their primary jobs.
Inline vs. Post-Process Deduplication
Next up is timing. Do you deduplicate data in real-time as it's being written, or do you handle it later as a background chore?
Inline deduplication is the real-time operator. It identifies and eliminates redundant data as it's being written to the storage system. This is incredibly efficient because duplicate data never even hits the disk. The trade-off? It can add a tiny bit of latency to write operations since the system has to check for duplicates on the fly.
On the other hand, post-process deduplication takes a "write now, sort later" approach. All data is written to the storage system first. Then, during a quiet period, the system scans the new data, finds the duplicates, and frees up the space. This means your write performance is never affected, but you need enough storage capacity upfront to hold all the raw, undeduplicated data temporarily.
To make these distinctions clearer, here's a quick look at how the different implementation methods stack up.
Comparing Deduplication Implementation Methods
This table breaks down the core methods, helping you see where each one shines.
| Method | When It Happens | Primary Advantage | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source-Side | Before data leaves the client/server | Reduces network bandwidth | Backing up remote offices; cloud replication |
| Target-Side | After data arrives at the storage system | Offloads processing from clients/servers | High-performance environments; centralized storage |
| Inline | In real-time, as data is written | Maximizes storage efficiency instantly | Primary storage; all-flash arrays |
| Post-Process | As a scheduled background task | No impact on initial write performance | Large backup archives; secondary storage |
Choosing the right combination of these methods is key to building an effective storage strategy that balances performance with cost savings.
File-Level vs. Block-Level Granularity
This might be the most important distinction of all because it determines just how much space you can actually save. The granularity—the level of detail—matters. A lot.
File-level deduplication is the simpler of the two, but block-level is where the real efficiency gains are found.
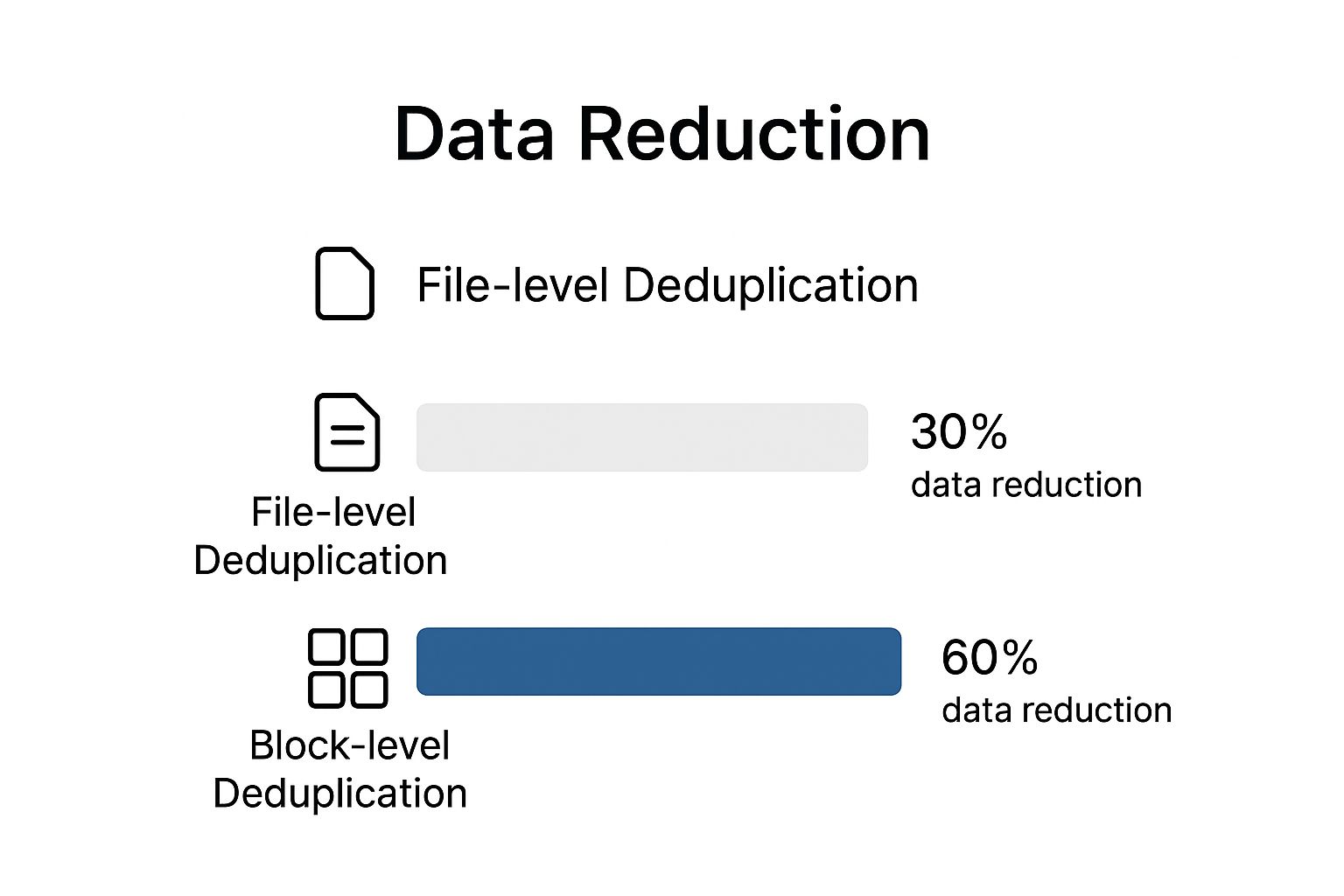
As you can see, the savings from block-level deduplication can often be double what you'd get from just looking at whole files.
Block-level deduplication is the engine behind most modern storage efficiency. It doesn't just look for identical files; it finds identical pieces of data inside different files, unlocking a much deeper level of savings.
Let's zoom in on how they work.
-
File-Level Deduplication: Also known as Single-Instance Storage (SIS), this method is straightforward. It finds identical files and stores only one copy. If you have the same PDF report saved in ten different folders, SIS stores it once and uses pointers for the other nine. The catch? If you change a single comma in one of those files, the system sees it as a brand-new, unique file and stores a full second copy.
-
Block-Level Deduplication: This is where things get much smarter. The system breaks files down into small, fixed-size chunks called "blocks." It then compares these individual blocks across the entire storage pool. This means it can find and eliminate duplicate data even if it’s buried inside two completely different files. For instance, if multiple PowerPoint decks use the same company logo, block-level deduplication stores the blocks for that logo image just one time.
The Real Business Benefits of Deduplication

While the tech behind deduplication is interesting, what really matters are the tangible results it brings to the business. The most obvious win, and the one everyone talks about first, is a massive reduction in storage needs. This isn't just about tidying up; it's about direct cost savings.
Storing less data means spending less on everything—physical drives, cloud storage bills, and even the electricity to keep it all running. This efficiency is key to smart IT budgeting. In fact, its power to shrink storage expenses is a big reason why intelligent automation solutions that reduce costs often incorporate deduplication. For many companies, this is the main justification for getting on board.
But the financial perks are just the tip of the iceberg. The improvements to your day-to-day operations, especially around backup and recovery, are often where the real magic happens.
Supercharged Backup and Recovery Speeds
Trying to back up terabytes of the same data over and over is a slow, expensive grind that clogs up your network. Deduplication shrinks the dataset before the backup, making the entire process faster and far more efficient. This isn't just a nice-to-have; it’s fundamental to business continuity.
With faster backups, you can run them more often. This closes the gap between snapshots, meaning less potential for data loss if something goes wrong. More importantly, when disaster strikes, restoring from a lean, deduplicated backup is worlds faster. This directly impacts your ability to hit crucial recovery targets:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): How quickly you need your systems back online. Faster restores mean a lower, better RTO.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The maximum amount of data you can stand to lose. More frequent backups shrink your RPO to minutes instead of hours.
Enhanced Network Performance and Data Mobility
It’s not just about storage; deduplication frees up your network, too. When you only have to move unique chunks of data across the wire, everything just flows better. This is a game-changer for disaster recovery (DR) plans that require replicating data to an offsite location.
Instead of jamming your network for hours trying to sync massive datasets, you’re sending a much smaller, deduplicated version. This efficiency makes it practical to replicate data far more frequently, keeping your DR site almost perfectly in sync. What used to be a resource-hogging nightmare becomes a smooth background task.
By minimizing data redundancy, deduplication doesn't just save disk space; it liberates network bandwidth, accelerates recovery, and simplifies data governance, making IT infrastructure more agile and resilient.
Simplified Management and Stronger Governance
Let's be honest: a smaller dataset is just plain easier to manage. When you don't have countless copies of the same files scattered everywhere, your IT team spends less time on tedious storage admin and more time on what matters. This cleanup also has a huge impact on data governance and compliance.
Auditing a clean, organized dataset is quicker and far more accurate. A smaller data footprint also means a smaller attack surface, which makes securing sensitive information much more manageable. This kind of operational clarity is foundational for companies aiming to build stronger data controls, a key component of effective business intelligence best practices. At the end of the day, a deduplicated environment is a more secure and governable one.
Where Deduplication Delivers the Most Value
The theory behind data deduplication is great, but its real power clicks into place when you see it solve actual business problems. Some IT environments are almost perfectly suited for this technology, offering huge efficiency gains that fix very specific, very common headaches. These aren't just niche applications; they're at the very core of how modern businesses operate.
The market certainly reflects this value. By 2025, the data deduplication software market is projected to hit around $2.5 billion. This isn't surprising when you consider the explosion of business data and tighter regulations pushing companies to find smarter ways to manage storage. You can dive deeper into the numbers by checking out the Data Deduplication Software Market growth report.
So, let's break down the key scenarios where deduplication really pays off.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
If there's one classic use case for data deduplication, it's backup and disaster recovery (DR). Think about it: without dedupe, most companies run full backups that copy massive amounts of the same data over and over, day after day. This chews through expensive storage and makes both backing up and restoring a painfully slow ordeal.
Deduplication completely changes the game. By only saving the unique chunks of data from each backup, organizations can slash their storage footprint.
- Longer Retention: You can afford to keep more historical backups online for longer, without your storage budget spiraling out of control.
- Faster Restores: A smaller, cleaner backup dataset means you can get critical systems back online much faster, which is crucial for hitting those demanding Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs).
- Efficient Replication: Copying deduplicated data to a disaster recovery site uses a fraction of the network bandwidth, making it practical to replicate backups far more frequently.
Virtual Environments
Virtualization is another area where deduplication is a game-changer, especially for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI). A standard VDI setup might have hundreds or thousands of virtual machines, and nearly all of them are running the exact same operating system. This creates a staggering amount of redundant data.
A single VDI environment can contain thousands of copies of the same core OS files. Deduplication identifies this massive overlap and stores only one unique instance, reclaiming huge amounts of primary storage space.
By getting rid of all those duplicate OS and application files, deduplication frees up a ton of your most expensive, high-performance storage. This makes the whole virtual environment cheaper to run and simpler to manage. It's a perfect example of how knowing what data deduplication is can directly impact your infrastructure costs.
Primary Storage and File Servers
Deduplication isn't just for backups and secondary storage. It can bring enormous value to your primary storage systems, too, especially on file servers and collaboration platforms. In these environments, people are constantly saving slightly different versions of the same documents, presentations, and spreadsheets.
File-level or block-level deduplication can spot and consolidate these duplicate files and data blocks as they're being saved. This keeps your primary storage lean and efficient, pushing back the need for expensive hardware upgrades. It helps ensure your most active and critical storage is optimized for both speed and capacity.
Common Questions About Data Deduplication
Even after getting the hang of the basics, some practical questions always pop up when it comes to data deduplication. It's a technology that touches everything from your storage and performance to the core integrity of your data, so it makes sense to dig into the details.
Let's tackle some of the most common things people ask.
Is Data Deduplication the Same as Compression?
This is a big one, and it's easy to see why people get them mixed up. They both save space, but they do it in completely different ways.
Think of compression like creating a shorthand for a single document. It looks for repetitive patterns inside that one file and shrinks it down.
Data deduplication, on the other hand, thinks bigger. It looks for identical chunks of data or even entire files across your entire system—thousands of them—and makes sure only one unique copy is ever stored. They actually make a great team; many systems will deduplicate data first, then compress the unique blocks that are left to get the absolute best space savings.
Does Deduplication Slow Down Performance?
The honest answer? It can, but how much really depends on the method.
Inline deduplication, which checks for duplicates as data is being written, can add a tiny bit of latency. The system has to pause and run a quick check for every single write operation. It’s happening in real-time, after all.
Then you have post-process deduplication, which flips the script. It writes all the new data first and then circles back later—usually during off-peak hours—to find and remove the duplicates. This keeps your initial write speeds zippy, but you need enough storage to hold all that new data before it gets cleaned up. Modern systems are so well-optimized with fast hardware that the performance hit is often barely noticeable.
One of the biggest worries with deduplication is what happens if a unique block of data gets corrupted. Since thousands of files might all point to that one block, robust data integrity checks are absolutely essential.
What Happens If a Unique Data Block Is Corrupted?
This is a critical question, and for good reason. If a single block referenced by thousands of files goes bad, you could be in a world of hurt. That’s why any enterprise-grade deduplication system is built with powerful safeguards.
These systems use advanced hashing algorithms and checksums (like SHA-256) to constantly verify that the data is intact. If a corrupted block is ever found, the system can usually restore it from a replica or a secondary backup copy, ensuring all the files pointing to it are safe. When you're choosing a solution, always prioritize one with strong self-healing and data protection features.
Is Deduplication Effective for All Data Types?
Definitely not. Deduplication works its magic on redundant data, which makes it a home run for certain types of files but a waste of time for others.
It’s incredibly effective for:
- Virtual machine files (VMDKs, VHDs): These are packed with identical operating system and application files across many different VMs.
- Full system backups: Week after week, full backups contain huge amounts of overlapping data that deduplication can easily spot and eliminate.
- User home directories: Think about how many duplicate documents, presentations, and other common files are scattered across your network.
On the flip side, it provides almost zero benefit for data that's already unique or compressed. This includes encrypted files, most video formats (MP4), audio files (MP3), and many image files (JPG). Smart storage systems can actually identify these file types and just skip them, saving valuable processing power. Keeping your data organized is also key, a topic we cover in our guide on data quality best practices.
Ready to stop wasting time on manual spreadsheet tasks? Elyx.AI integrates powerful AI analysis, translation, and cleaning tools directly into Excel, letting you generate insights with simple text commands. Streamline your workflow and unlock the full potential of your data by visiting https://getelyxai.com to get started.