What Is Data Parsing? A Practical Guide for Excel Users

Data parsing is the process of converting messy, unstructured data into a clean, organized format that software can understand. It's the critical first step that allows tools like Excel to read, analyze, and extract value from your information. Without it, your data is often just a jumbled mess.
What Is Data Parsing in Simple Terms?
Imagine trying to follow a recipe where all the ingredients and instructions are crammed into one long, run-on sentence. No line breaks, no bullet points, no clear measurements—just a wall of text. It would be nearly impossible to use. That’s what raw data often looks like to Excel. It's a chaotic stream of information that the software can't interpret on its own.
Data parsing is the art of adding that missing structure. It's like being an editor for your data. You add the "punctuation" (like commas or tabs, known as delimiters) and create "paragraphs" (like columns and rows) to bring order to the chaos. This process transforms a jumbled string of text into a neat, clean table that Excel can finally work with.
Spending too much time on Excel?
Elyx AI generates your formulas and automates your tasks in seconds.
Try for free →
From Chaos to Clarity: An Excel Example
Let's say you have a single cell in Excel (A1) containing "John Doe, 123 Main St, Anytown, USA, 12345". To you, that’s a complete address. But to Excel, it's just one long piece of text. If you wanted to sort your contacts by city or filter everyone by a specific zip code, you couldn't do it with the data in this state.
Data parsing is the bridge between raw data and actionable insight. It doesn't change the information itself; it changes how that information is structured, making it accessible for analysis, reporting, and decision-making within tools like Excel.
The need for this became undeniable as digital information exploded. Back in 2010, the world was already generating an estimated 2.5 quintillion bytes of data daily. Sifting through that mountain of information to find anything valuable made parsing an essential business skill. For more context, you can explore the history of data collection and how it shapes modern business.
To make this concept crystal clear, here’s a quick before-and-after snapshot of what data parsing accomplishes in a spreadsheet context.
Data Parsing At a Glance
| Concept | Raw Data Example (Before Parsing) | Structured Data Example (After Parsing in Excel) |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Info | Cell A1: JaneSmith,[email protected],555-1234 |
Column A (Name): Jane Smith Column B (Email): [email protected] Column C (Phone): 555-1234 |
| Product Data | Cell A1: "Laptop-15" - $999.99 [SKU:LP15-001] |
Column A (Product): Laptop-15 Column B (Price): 999.99 Column C (SKU): LP15-001 |
| Log Files | Cell A1: 2023-10-26 10:00:00 ERROR:Login Failed |
Column A (Timestamp): 2023-10-26 10:00:00 Column B (Level): ERROR Column C (Message): Login Failed |
As you can see, parsing takes jumbled text and breaks it down into distinct, meaningful pieces of information that can be easily managed in separate Excel columns.
Why Parsing Is a Foundational Skill in Excel
For anyone who works with data in Excel, learning how to parse it is a superpower. It's the first and most important step for nearly any task, whether you're creating a simple chart, building a complex financial model, or preparing data for an AI-powered analysis.
If you skip this step or do it poorly, your analysis will be built on a shaky foundation, leading to flawed reports and unreliable insights. Proper parsing ensures your data is:
- Structured: Information is sorted into the right columns, like putting
Anytownin the "City" column and12345in the "Zip Code" column. - Usable: Once structured, Excel can finally do its job—running calculations, sorting A-Z, or filtering for specific criteria.
- Consistent: Data formats are standardized across your entire dataset, which is crucial for accurate and dependable analysis.
The Core Techniques of Data Parsing
So, you understand that data parsing is about turning chaos into order. That's the big picture. Now, let’s explore the actual tools and techniques that make it happen in Excel. Think of these as your data toolkit, each one suited for a specific cleanup job, from splitting a simple column to hunting down complex patterns.
This whole idea of parsing isn't new; it’s been around since the early days of computer science. Back in the 1960s, researchers were wrestling with how to turn raw computer code into commands a machine could understand. They came up with clever solutions like stack-driven parsing algorithms, which by 1961 were the go-to method because they were fast without hogging memory—a balance that paved the way for modern software.
Delimiter-Based Parsing
This is the most common technique you'll use in Excel and the easiest to grasp. It works by identifying a specific character—a delimiter—that acts as a divider between pieces of information. It's just like using commas to separate items in a list.
Here are a few common delimiters:
- Commas (,): The classic, found everywhere in CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files. Think
FirstName,LastName,Email. - Tabs (\t): Often used when you copy and paste data from databases or text files.
- Spaces ( ): Perfect for separating words, like first and last names.
- Pipes (|): A less common but reliable choice because they rarely appear within the data itself.
Let's say a marketing tool exports a list of contacts as "John Doe, 123 Main St, Anytown, USA 12345" in a single cell. A parser using a comma delimiter instantly sees the commas and splits that single string into five neat fields: Name, Street, City, Country, and Zip Code, each in its own column. It's a fundamental skill, and you can see it in action in our guide on how to split text in Excel.
Fixed-Width Parsing
What happens when there are no delimiters? This is where fixed-width parsing comes in. This method is for data where information is aligned in columns of a specific, unchanging length. Imagine an old report where the first 10 characters are always the account number, the next 20 are the customer's name, and the final 5 are the zip code.
A fixed-width parser doesn't look for a separator. It simply counts characters from the start of the line and makes a cut at predefined positions. It's a rigid approach but incredibly reliable for structured legacy data where consistency is guaranteed.
Key Takeaway: Use delimiter-based parsing when your data has consistent separators. Opt for fixed-width parsing when your data is laid out in columns of a set size with no delimiters.
Regular Expressions (Regex)
When your delimiters are inconsistent and the column widths are unpredictable, you need a more powerful tool. Regular Expressions, or Regex, are text strings used to define a search pattern. Instead of looking for a simple comma, you can write a rule as specific as, "find any five-digit number that appears immediately after the word 'Code:'."
Regex is the Swiss Army knife of data parsing. It can extract email addresses from a messy text block, find all phone numbers regardless of their formatting—(555)-123-4567 or 555.123.4567—or pull product SKUs from long descriptions. While Regex has a steeper learning curve, mastering it allows you to parse almost any unstructured text imaginable.
Handling Structured Formats like JSON and XML
Today, much of the data exchanged between applications is already organized in structured formats like JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) or XML (eXtensible Markup Language). These formats use their own rules—like curly braces {} in JSON or tags <tag> in XML—to create a clear data hierarchy.
Parsing these files in Excel means using tools like Power Query to read that specific structure and translate it into a familiar table. For instance, a parser can read a JSON object with customer details and map each key-value pair (like "name": "Jane Doe") to the correct column in your spreadsheet. To see how data is pulled and structured from scratch, it’s worth checking out how to build a simple web scraper with Python and export to CSV.
Mastering Data Parsing in Excel Step by Step
Knowing the theory is one thing, but actually parsing data in Excel is where you gain real skills. Let's move from concepts to practical application. We'll walk through three essential methods for taming messy data, empowering you to confidently tackle any dataset.
First, we'll cover the simple but powerful 'Text to Columns' feature, perfect for quick, one-off jobs. Next, we'll get more precise with text formulas like LEFT, RIGHT, and MID to extract exactly what you need. Finally, for heavy-duty, repeatable tasks, we'll unleash Power Query, Excel's data transformation powerhouse.
This flowchart provides a quick visual guide to selecting the right tool for the job.
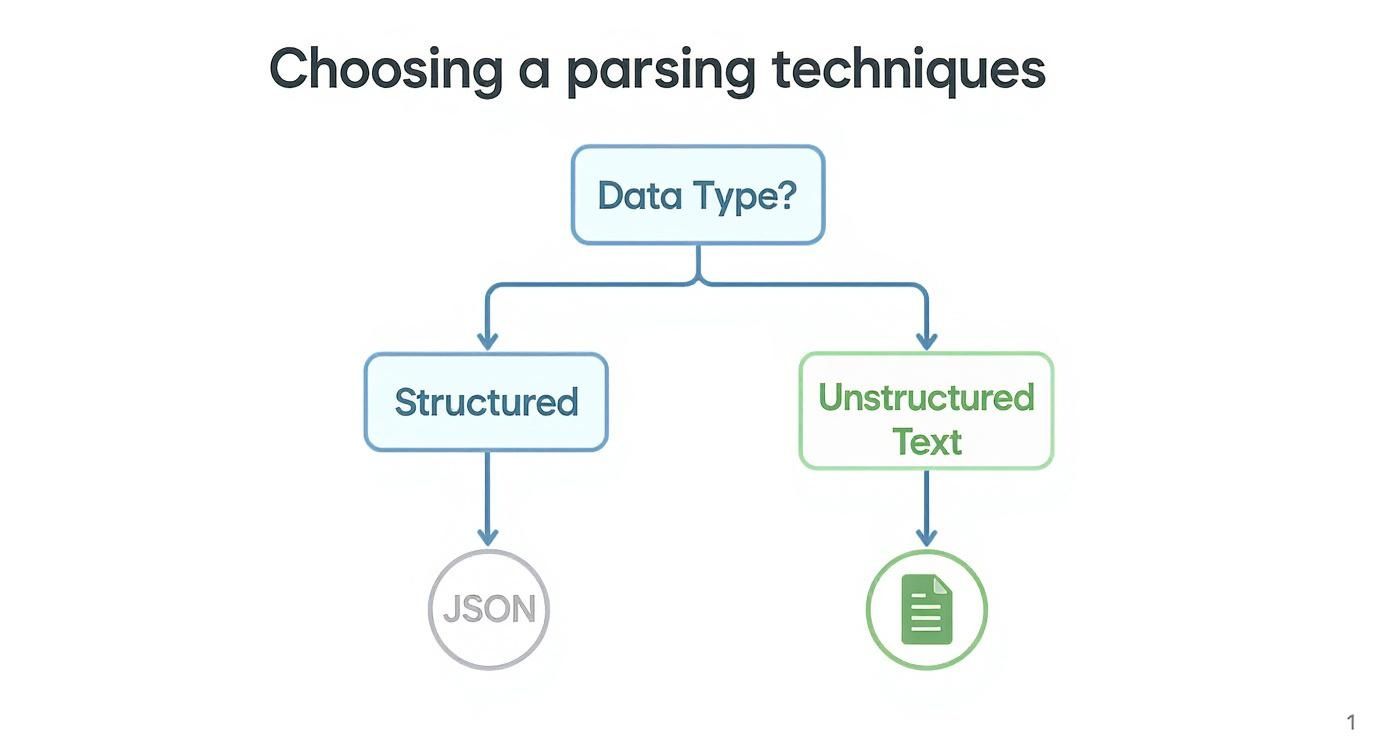
As you can see, the process starts with a simple question: is your data structured or unstructured? The answer points you in the right direction.
Method 1: The Simplicity of Text to Columns
Think of 'Text to Columns' as your go-to tool for a quick and clean split. It’s perfect when your data is separated by a consistent delimiter like a comma, space, or tab. This is the fastest way to get from a jumbled mess in one column to neatly organized data across multiple columns, with no formulas required.
Let's say you have a column (A) full of names like "John Smith" and you want to separate them into first and last names in columns B and C.
Here’s how to do it in just a few clicks:
- Select Your Data: Highlight the column with the text you want to split (column A).
- Open the Wizard: Go to the Data tab on the Excel ribbon and click Text to Columns.
- Choose Your Data Type: The wizard will appear. Select Delimited and click Next. This tells Excel that a specific character is separating your data.
- Set Your Delimiter: On the next screen, specify the delimiter. For "John Smith," you would check the Space box. You'll see a live preview of the split. If it looks correct, click Next.
- Finalize the Split: Choose the destination for your new data (e.g., cell B2) and click Finish.
And that’s it. In just five clicks, Excel neatly places "John" in column B and "Smith" in column C. It's incredibly efficient for one-off data cleaning tasks.
Method 2: Surgical Extraction with Text Formulas
Sometimes you don't need to split an entire cell; you just need to extract a specific piece of information from a string. This is where Excel's text functions excel, allowing you to perform precise, surgical extractions.
The real beauty of formulas is their dynamic nature. While 'Text to Columns' is a one-time action, formulas create a living link to your source data. Change the original cell, and the formula updates automatically.
Let's take a common scenario: you have a product description like "SKU: PN-54321 – Blue Widget" in cell A2, and you only need the product code, "PN-54321".
These functions will be your best friends:
- LEFT(text, num_chars): Extracts a set number of characters from the start of a text string.
- RIGHT(text, num_chars): Extracts characters from the end of a text string.
- MID(text, start_num, num_chars): Pulls characters from the middle of a string.
- FIND(find_text, within_text): Locates the starting position of one text string within another.
To extract "PN-54321", you can combine MID and FIND into a clever formula: =MID(A2, FIND(":", A2)+2, 8). This tells Excel to find the colon, move two spaces forward, and then grab the next eight characters.
This level of precision is invaluable, especially for tasks like extracting data from PDF into Excel, where information is often buried inside larger blocks of text.
Method 3: Automation with Power Query
When you find yourself performing the same parsing steps repeatedly or when dealing with large datasets, formulas can become cumbersome. Enter Power Query. It’s a data transformation engine built into Excel that lets you create a repeatable, automated workflow for cleaning and parsing data.
Think of it as recording a macro, but specifically for data preparation. Power Query remembers every step you take—splitting columns, removing characters, changing formats—and saves it as a "query." The next time you get a new file with the same structure, you just hit "Refresh," and Power Query performs all the steps for you. It's a massive time-saver and eliminates the risk of human error.
Imagine you receive a messy sales report every month that requires the same cleanup process.
Here’s how you’d build an automated parsing workflow with Power Query:
- Load Data into Power Query: Select your data, go to the Data tab, and click From Table/Range. This will launch the Power Query Editor.
- Apply Transformations: Inside the editor, use the user-friendly interface to split columns, replace values, trim spaces, or change data types. Every action is recorded in the "Applied Steps" pane on the right.
- Load the Clean Data: Once your data looks perfect, click Close & Load. Power Query will place the clean, transformed data into a new worksheet.
Next month, when the new report arrives, you just right-click your new data table and hit Refresh. All those cleaning steps are executed in seconds. To get a better feel for its capabilities, our complete Excel Power Query tutorial is a great place to start.
Comparing Excel Data Parsing Methods
Choosing the right tool for the job makes all the difference. This table breaks down which method to use based on task complexity, frequency, and ease of use.
| Method | Best For | Ease of Use | Reusability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text to Columns | Simple, one-time data splits with a consistent delimiter. | Very Easy | Low (Manual process) |
| Formulas (LEFT, MID, etc.) | Precise, dynamic extractions from text strings that need to auto-update. | Medium | High (Can be copied down) |
| Power Query | Complex, multi-step, and repeatable data cleaning tasks on large datasets. | Medium to Advanced | Very High (Automated workflow) |
In short, start with Text to Columns for quick, simple tasks. Graduate to formulas when you need more control and dynamic results. And when you're tired of repeating the same cleaning process, it's time to let Power Query automate your workflow.
How AI Is Changing Data Parsing in Excel
While traditional methods like Text to Columns and Power Query are powerful, they have a learning curve. You need to know which formulas to write or how to navigate complex menus. This is where Artificial Intelligence is transforming how we handle data in Excel.
AI tools that integrate directly into your spreadsheet act as intelligent assistants. Instead of figuring out the exact steps yourself, you simply describe what you want in plain English. This paradigm shift makes powerful data parsing accessible to everyone, not just Excel experts.
From Complex Formulas to Simple Conversations
The real magic of AI-driven parsing lies in shifting your focus from the how to the what. You no longer have to struggle with a complicated formula like =MID(A2, FIND(":", A2)+2, 8) just to extract a product code. You can simply ask for it.
Let's say you have a column of messy product descriptions. With an AI tool like Elyx.AI, you could type a simple instruction:
"Extract all 5-digit product codes that start with 'P' from column B and place them in column C."
The AI understands the pattern you’re describing and performs the task instantly. This conversational approach eliminates trial-and-error with formulas and the need to navigate through Power Query options. You can stay focused on your analysis instead of getting bogged down by the mechanics.
The Power of Natural Language in Data Parsing
This is made possible by natural language processing (NLP), a technology that allows AI to understand human language, context, and intent. It’s a game-changer for parsing tasks that are difficult to handle with strict rules.
Consider these common challenges that AI solves with ease:
- Handling Inconsistent Data: What if some codes are formatted as
P-12345while others areProduct: 12345? A standard formula would likely fail, but an AI can recognize that they represent the same type of data. - Extracting Multiple Elements at Once: You could ask the AI to "Pull the product name, price, and SKU from each cell in column A," and it would intelligently split all three into new columns for you.
- Interpreting Vague Requests: An AI can make sense of commands like, "Find all the email addresses in this text," without requiring you to provide a complex regular expression.
This ability to work with messy, unstructured information is a significant leap forward from traditional methods. To dive deeper into how this works, check out our guide on AI for Excel.
AI as a Co-Pilot for Your Data
Think of AI in Excel as a co-pilot for your data work. It doesn't replace your judgment, but it handles the tedious heavy lifting of parsing, cleaning, and structuring your information. This frees up your mental energy for what truly matters: identifying trends, building reports, and making informed decisions.
The result is a workflow that is not only faster but also more intuitive. By simply describing your goal, you can accomplish in seconds what used to take minutes or even hours of painstaking work. This isn't just a minor improvement—it’s a fundamental change in how we interact with data in spreadsheets.
Solving Common Data Parsing Challenges
Let's be honest: real-world data is rarely clean. It's often a chaotic mix of inconsistent formats, missing information, and frustrating errors that can halt your analysis. Knowing what is data parsing is one thing, but knowing how to troubleshoot these common issues is what transforms messy data into a reliable asset.
This is where your skills are truly tested. You might receive a file where one person used commas as separators while another used semicolons. Or perhaps you've encountered a single column with mixed date formats like ‘01-15-2024’ and ‘Jan 15, 24’. These inconsistencies can break your formulas and invalidate your reports.

Tackling Inconsistent Delimiters
One of the most common headaches is dealing with different delimiters in the same dataset. Imagine a column of contact info with entries like Doe, John; 555-1234 and Smith, Jane, 555-4321. A simple "Text to Columns" split in Excel won't work correctly here.
Excel Solution: Power Query
For this kind of problem, Power Query is your best friend. Instead of a one-shot split, you build a quick, multi-step process. First, you can tell it to replace all semicolons with commas to standardize the delimiter. Then, you can perform a clean split by the comma, ensuring every entry is parsed correctly.
AI-Assisted Solution
An AI tool like Elyx.AI simplifies this even further. You just tell it what to do in plain English:
"In column A, replace all semicolons with commas, then split the text into separate columns."
The AI handles the entire process in one go, saving you from navigating multiple menus.
Correcting Tricky Date Formats
Mixed date formats are another classic problem. Excel often gets confused by dates written in different ways and treats them as text, which means you can't sort by date or perform time-based calculations.
Excel Solution: Format Cells & Formulas
If Excel recognizes the date but displays it incorrectly, the "Format Cells" option is an easy fix. But if the format is completely non-standard (like '15-Jan/2024'), you'll need to construct formulas using functions like DATE, LEFT, MID, and RIGHT to piece a valid date together.
AI-Assisted Solution
This is where AI truly shines. You can give it a simple instruction and let it handle the complexity:
"Convert all the different date formats in column C to a standard 'MM/DD/YYYY' format."
The AI is smart enough to recognize a wide variety of date patterns and unify them for you, no complex formulas needed.
Handling Missing or Null Values
Blank cells, or null values, can cause all sorts of problems, leading to errors like #VALUE! or #DIV/0!. If left unaddressed, they can skew averages and other statistical calculations, compromising the integrity of your analysis.
Dealing with imperfect data isn't new. This has been a core challenge since pioneers like Anders Nicolai Kiær introduced new sampling methods back in 1895. The accuracy of modern insights still depends on how well we handle these imperfections. You can read more about the history of statistics and its evolution to see how far we've come.
Here’s how to manage those empty cells in Excel:
- Identify Blanks: A quick trick in Excel is the "Go To Special" feature (F5 > Special > Blanks). This instantly highlights every empty cell in your selection.
- Fill or Replace: Once highlighted, you must decide how to handle them. Should they be zero? "N/A"? Or perhaps the average of the column? The choice depends on what makes sense for your analysis.
- AI-Powered Cleaning: An AI can automate this. A prompt like, "Find all empty cells in the 'Sales' column and fill them with 0," ensures every blank is handled consistently without manual intervention.
Got Questions About Data Parsing? We’ve Got Answers.
Let’s tackle some of the most common questions that arise when people start parsing data. These quick answers should clear up any confusion and help you apply these techniques effectively in Excel.
Data Parsing vs. Data Cleaning: What's the Real Difference?
It’s easy to confuse these two terms, but they represent different stages of data preparation. Think of it like cooking a meal.
Data parsing is the prep work, like chopping the vegetables. You’re taking raw, unstructured ingredients (a whole carrot) and breaking them down into a specific, usable format (diced pieces). It’s all about creating the right structure.
Data cleaning, on the other hand, is the entire cooking process. It includes parsing, but it also involves removing spoiled ingredients (correcting errors), discarding duplicates, and filling in for missing items. Parsing is a crucial first step, but cleaning is the comprehensive process of ensuring data quality.
When Should I Use Power Query Over Standard Excel Formulas?
This is a great question, and the answer depends on complexity and repetition.
Use Excel formulas for quick, one-off tasks. If you just need to split a column of names or extract a zip code from a few hundred rows, formulas are fast, direct, and effective without requiring extra setup.
Use Power Query when you find yourself repeating the same parsing tasks, especially with large datasets. It’s built for creating repeatable workflows, pulling data from multiple sources, and applying a series of transformations. Power Query records your steps, creating an automated process you can refresh with a single click.
Think of it this way: Formulas are your sharp knives for quick, precise cuts. Power Query is your automated food processor for big, recurring jobs.
Can AI Really Handle My Messy, Unique Data Structures?
Absolutely. In fact, this is where AI tools truly excel. A modern AI assistant can analyze complex, inconsistent data and identify the underlying patterns on its own—a task that might otherwise require a complicated formula or a sophisticated regular expression.
While you should always review the AI's work to ensure accuracy, for the most part, you can describe your goal in plain English, and the AI will handle the technical execution. This opens up advanced data parsing to any Excel user, regardless of their technical expertise.
Ready to stop wrestling with messy data and let AI do the heavy lifting? Elyx.AI plugs right into Excel, letting you parse, clean, and analyze your data with simple English commands. Transform your spreadsheets and find insights in seconds by checking out Elyx.AI.
Reading Excel tutorials to save time?
What if an AI did the work for you?
Describe what you need, Elyx executes it in Excel.
Try 7 days free